| –
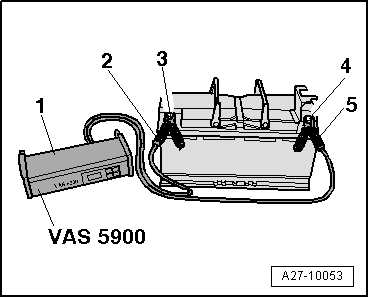
| Connect clamp -5- of positive cable of battery charger -1- to battery positive terminal post -4- and clamp -2- of earth cable of battery charger to battery earth terminal post -3-. |

Note | Illustration shows battery removed. |
| –
| Adjust the charging current on the charger according to the battery capacity. |
| l
| The charging current should be around 10 % of the battery capacity (so for a 60 Ah battery around 6 A). |
| –
| Switch on the battery charger. |
| Reassembly is carried out in the reverse order; note the following: |
| –
| Connect battery. Additional steps required → Anchor. |
| t
| Batteries which have not been used for lengthy periods, e.g. in vehicles which have not been driven, are subject to self-discharge. |
| t
| A battery is considered to be exhausted if the no-load voltage has dropped below 11.6 V. Initial battery damage can occur between 12.2 and 11.6 V. Measuring no-load voltage → Chapter. |
| t
| In an exhausted battery the electrolyte (sulphuric acid/water mixture) is reduced to almost all water, as the sulphuric acid content is heavily reduced. At temperatures below zero, the battery may freeze and the cause the housing to burst. |
| t
| Exhausted batteries become sulphated, i.e. the entire battery plate surfaces harden. The electroyte has a slightly milky appearance (instead of being clear). |
| t
| If exhausted batteries are charged directly after being discharged, the sulphation dissipates. |
| t
| If this is not done, the plates become even harder and the battery's ability to absorb charge is impaired. This results in reduced power output. |
| Procedure for charging exhausted batteries (sulphated) |
| Exhausted batteries (that are also sulphated) must be charged as follows using a low charging current: |
| –
| Approx. 5 % of battery capacity, i.e.for a 60 Ah battery the charging current is approx. 3 A. |
| Charging battery → Chapter. The charging voltage (Umax) must not exceed 14.4 V. |

Note | Do NOT attempt to rapid-charge exhausted batteries. |
|
|
|
 Note
Note
 Note
Note Note
Note

 Note
Note


 Note
Note Note
Note