XC70 AWD L6-3.2L VIN 98 B6324S (2009)
-
engine speed (RPM) sensor (7/25)
-
Camshaft sensor (7/172-173)
-
mass air flow (MAF) sensor (7/17)
-
engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor (7/16)
-
throttle position (TP) sensor on the electronic throttle unit (6/120)
-
knock sensor (KS) (7/23-24)
-
transmission control module (TCM) (4/28)
-
spark plugs with ignition coils (20/3-8).
The engine control module (ECM) calculates the optimum ignition advance based on the software and information from the sensors. The engine control
module (ECM) cuts the current to the ignition coil mounted on the cylinder to be ignited and produces a spark.
During the starting phase the engine control module (ECM) produces a fixed ignition setting. When the engine has started and the vehicle is being
driven, the engine control module (ECM) calculates the optimum ignition setting, taking factors such as the following into account:
-
engine speed (RPM)
-
load
-
temperature.
The engine control module (ECM) analyses the signal from the knock sensors (KS) when the engine reaches operating temperature. If any of the
cylinders knock, the ignition is retarded for that specific cylinder until the knocking ceases.
The ignition then advanced to the normal position or until the knock recurs.
Before the Transmission control module (TCM) is going to shift, sometimes it sends a request for torque limitation to the Engine control module (ECM).
Which then lowers the ignition momentarily to reduce the torque and thus give smoother shifting and reduced load on the transmission.
Lowering of ignition can be done in several levels, where the levels depend on the signals from the Transmission control module (TCM). The return
signal from the Engine control module (ECM) to the Transmission control module (TCM) confirms that the signal reached the Engine control module
(ECM).
For further information, also see: Misfire diagnostic See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control Systems/Description and Operation/Misfire
Diagnostic
The engine misfires if the fuel does not ignite correctly. For further information, also see: Misfire diagnostic See: Powertrain Management/Computers
and Control Systems/Description and Operation/Misfire Diagnostic
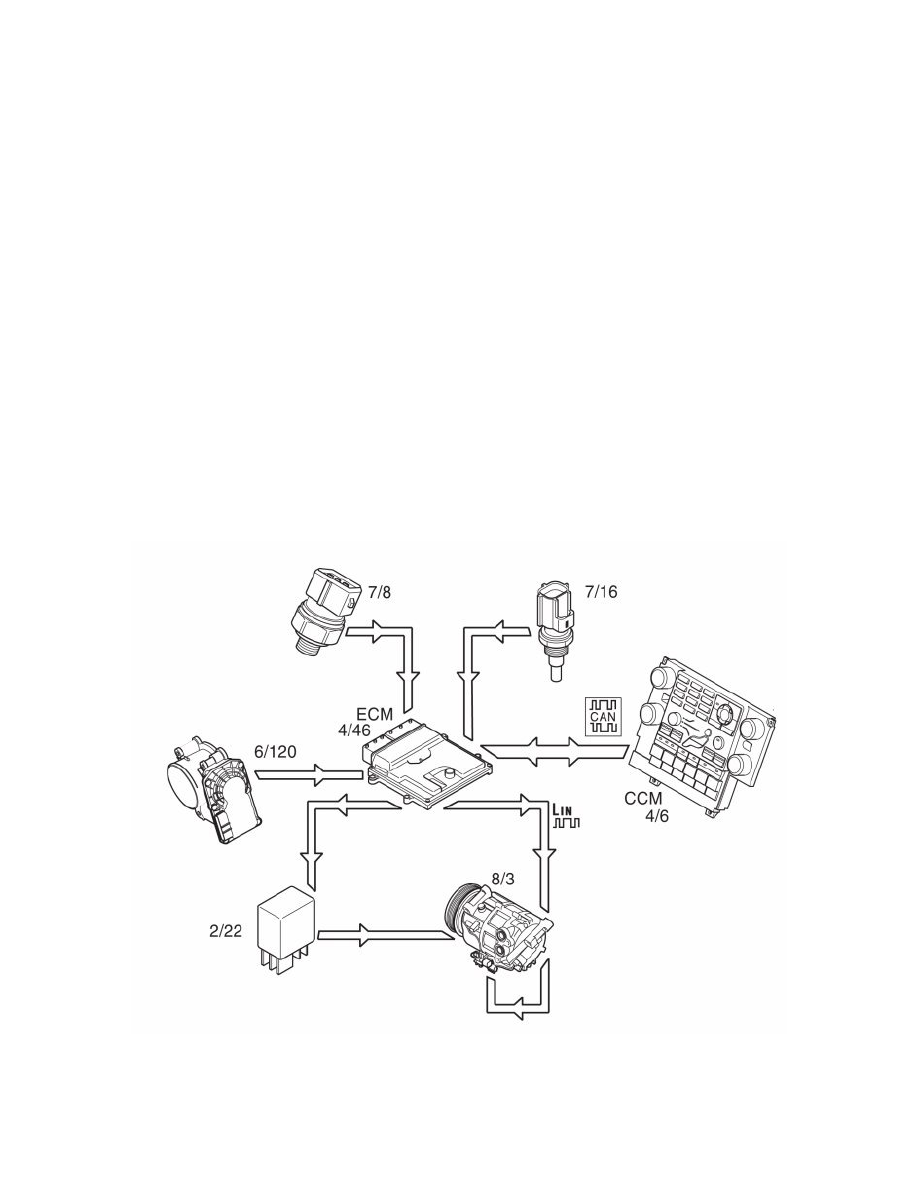
Regulating the air conditioning (A/C) compressor
The air conditioning (A/C) compressor is controlled by the engine control module (ECM) (4/46) on request from the climate control module (CCM)
(4/6) via the controller area network (CAN). When the engine control module (ECM) receives a signal from the climate control module (CCM) to
activate the air conditioning (A/C) compressor, the engine control module (ECM) grounds the circuit for the relay coil for the A/C compressor. See also:
Design See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control Systems/Description and Operation/Engine Control Module (ECM)/Design
The relay (2/22) closes the circuit between the integrated relay/fusebox in the engine compartment and the clutch for the air conditioning (A/C)
