Hombre XS Space Cab L4-2.2L CPC (1997)
Air Bag Control Module: Component Tests and General Diagnostics
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
When the supplemental restraint Diagnostic Energy Reserve Module (DERM) recognizes that the Ignition 1 voltage, applied to terminals A9 and
Al0, is in the normal operating voltage range, the AIR BAG warning lamp is flashed seven times to verify operation. At this time the DERM
performs Turn On tests followed by Continuous Monitoring tests. When no malfunctions are detected, the DERM proceeds to the Initiator
Assembly Resistance Test. When a malfunction is detected the DERM sets a current diagnostic trouble code and illuminates the AIR BAG
warning lamp. The DERM will clear current diagnostic trouble codes and move them to a history file when the malfunction is no longer detected
and/or the ignition switch is cycled, except for DTC B1051. DTC B1051 can only be cleared using a scan tool Clear Codes command.
Integrity Check Derm
TEST DESCRIPTION
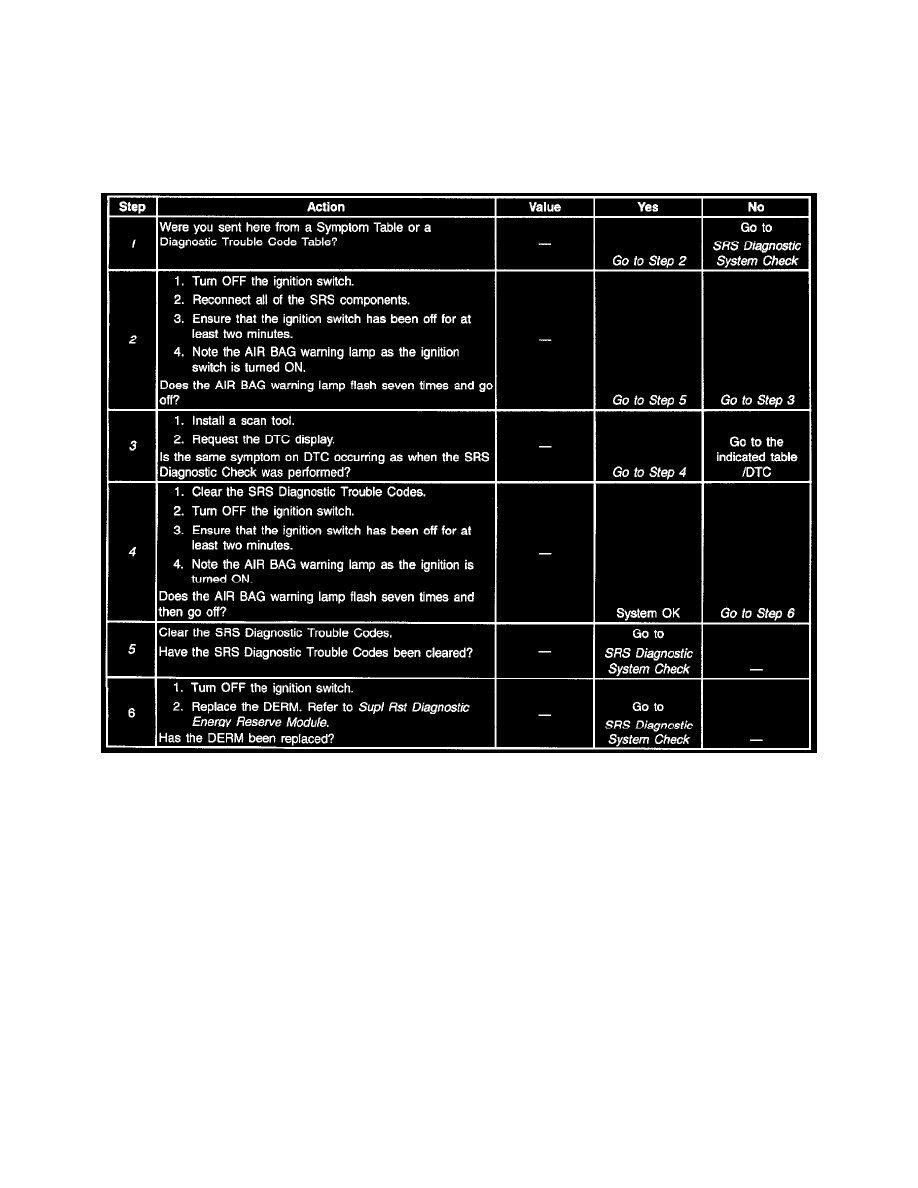
Refer to step numbers on the diagnostic table.
1. Start with the SRS Diagnostic System Check for all diagnosis.
2. This test confirms a current malfunction. If a History DTC set exists, reference the Diagnostic Aids for the appropriate DTC. Do not replace
the DERM for a History DTC.
3. This test checks for a malfunction introduced into the Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) during the diagnostic process. A malfunctioning
DERM is extremely unlikely to cause a new malfunction to occur during the diagnostic process.
4. Replace the DERM only when all circuitry outside the DERM has been found to operate properly as indicated by the appropriate diagnostic
table.
5. The symptom or DTC is no longer occurring. The condition may be intermittent or was inadvertently repaired during diagnosis of the
Supplemental Restraint System (SRS). Refer to Intermittents and Poor Connections.
