Rodeo S 2WD L4-2.2L (1999)
Catalytic Converter: Description and Operation
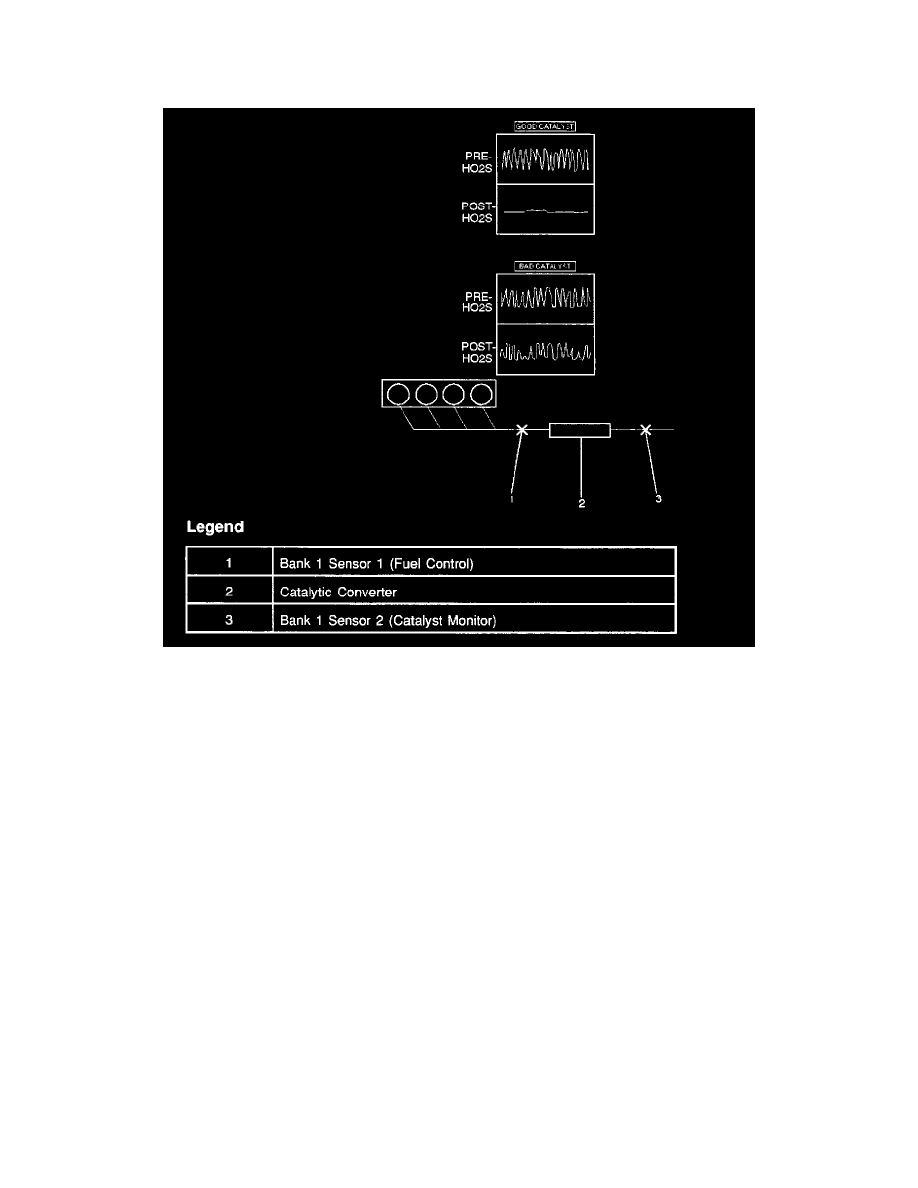
Three Way Catalytic Converter
Three-way catalytic converters are used to control emissions of hydrocarbons (HC), carbon monoxide (CO), and oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
The catalyst within the converters promotes a chemical reaction. This reaction oxidizes the HC and CO present in the exhaust gas and converts them into
harmless water vapor and carbon dioxide.
The catalyst also reduces NOx by converting it to nitrogen. The PCM can monitor this process using the Bank 1 HO2S 2 heated oxygen sensor. The
Bank 1 HO2S 1 sensor produces an output signal which indicates the amount of oxygen present in the exhaust gas entering the three-way catalytic
converter.
The Bank 1 HO2S 2 sensor produces an output signal which indicates the oxygen storage capacity of the catalyst. This indicates the catalysts ability to
efficiently convert exhaust gases. If the catalyst is operating efficiently, the Bank 1 HO2S 1 signal will be more active than the signal produced by the
Bank 1 HO2S 2 sensor.
The catalyst monitor sensors operate the same as the fuel control sensors. The Bank 1 HO2S 2 sensor's main function is catalyst monitoring, but it also
has a limited role in fuel control. If a sensor output indicates a voltage either above or below the 450 mV bias voltage for an extended period of time, the
PCM will make a slight adjustment to fuel trim to ensure that fuel delivery is correct for catalyst monitoring.
