Commander 4WD V8-4.7L VIN N (2006)
Brake Caliper: Description and Operation
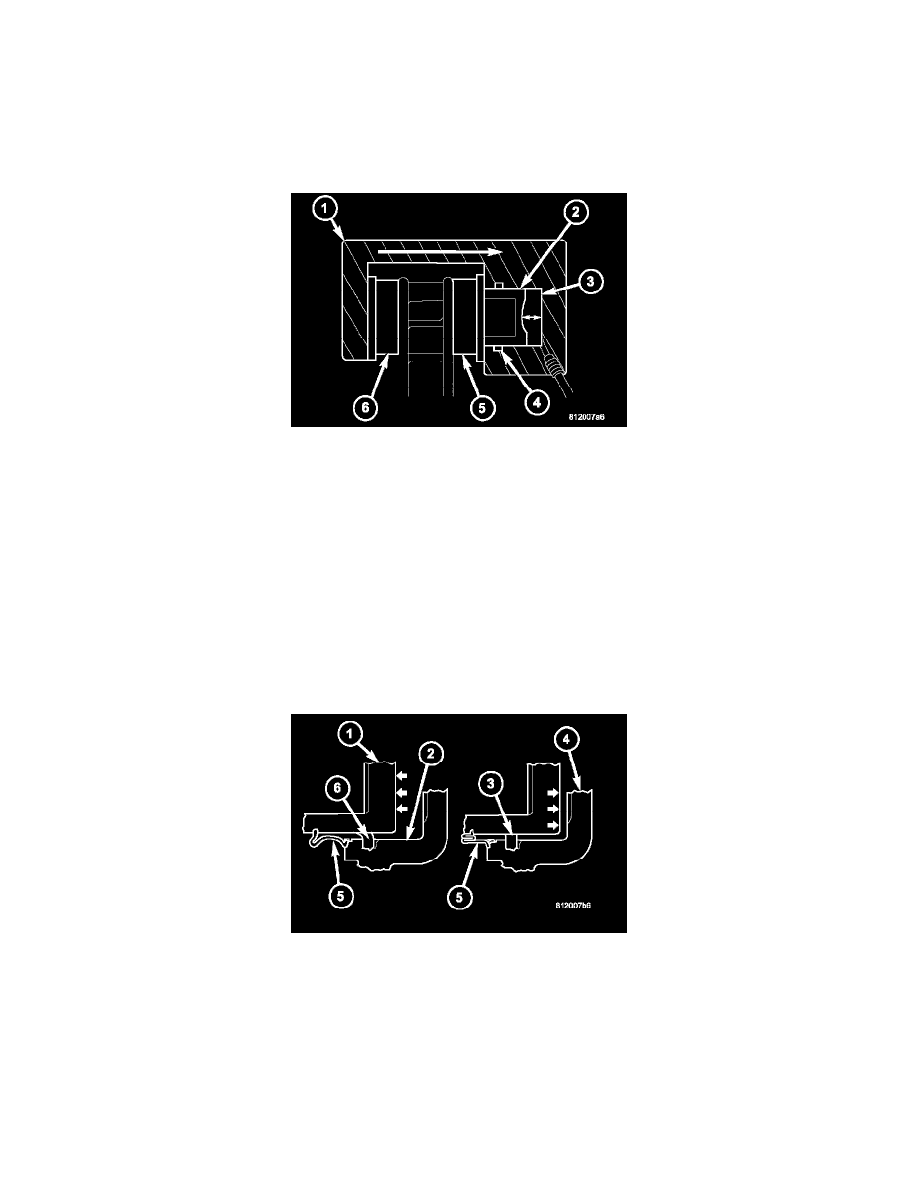
DISC BRAKE CALIPERS
DESCRIPTION
The calipers are a single piston type in the rear and dual piston type in the front. The calipers are free to slide laterally, this allows continuous
compensation for lining wear.
OPERATION
When the brakes are applied fluid pressure is exerted against the caliper piston (2). The fluid pressure is exerted equally and in all directions. This
means pressure exerted against the caliper piston and within the caliper bore will be equal.
Fluid pressure applied to the piston is transmitted directly to the inboard brake pad (5). This forces the pad lining against the inner surface of the disc
brake rotor. At the same time, fluid pressure within the piston bore forces the caliper to slide inward on the mounting bolts. This action brings the
outboard brake pad lining (6) into contact with the outer surface of the disc brake rotor.
In summary, fluid pressure acting simultaneously on both piston and caliper, produces a strong clamping action. When sufficient force is applied,
friction will attempt to stop the rotors from turning and bring the vehicle to a stop.
Application and release of the brake pedal generates only a very slight movement of the caliper and piston. Upon release of the pedal, the caliper and
piston return to a rest position. The brake pads do not retract an appreciable distance from the rotor. In fact, clearance is usually at, or close to zero.
The reasons for this are to keep road debris from getting between the rotor and lining and in wiping the rotor surface clear each revolution.
The caliper piston seal (4) controls the amount of piston (2) extension needed to compensate for normal lining wear.
During brake application, the seal is deflected outward by fluid pressure and piston movement (6). When the brakes (and fluid pressure) are released,
the seal relaxes and retracts the piston (3).
The amount of piston retraction is determined by the amount of seal deflection. Generally the amount is just enough to maintain contact between the
piston and inboard brake pad.
