Sportage 4WD L4-2.0L DOHC (1996)
Positive Crankcase Ventilation: Description and Operation
DESCRIPTION
The crankcase emission control system / Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system is a closed ventilation system that is designed to prevent
crankcase fumes or combustion gases from escaping through the engine oil filler cap to the atmosphere.
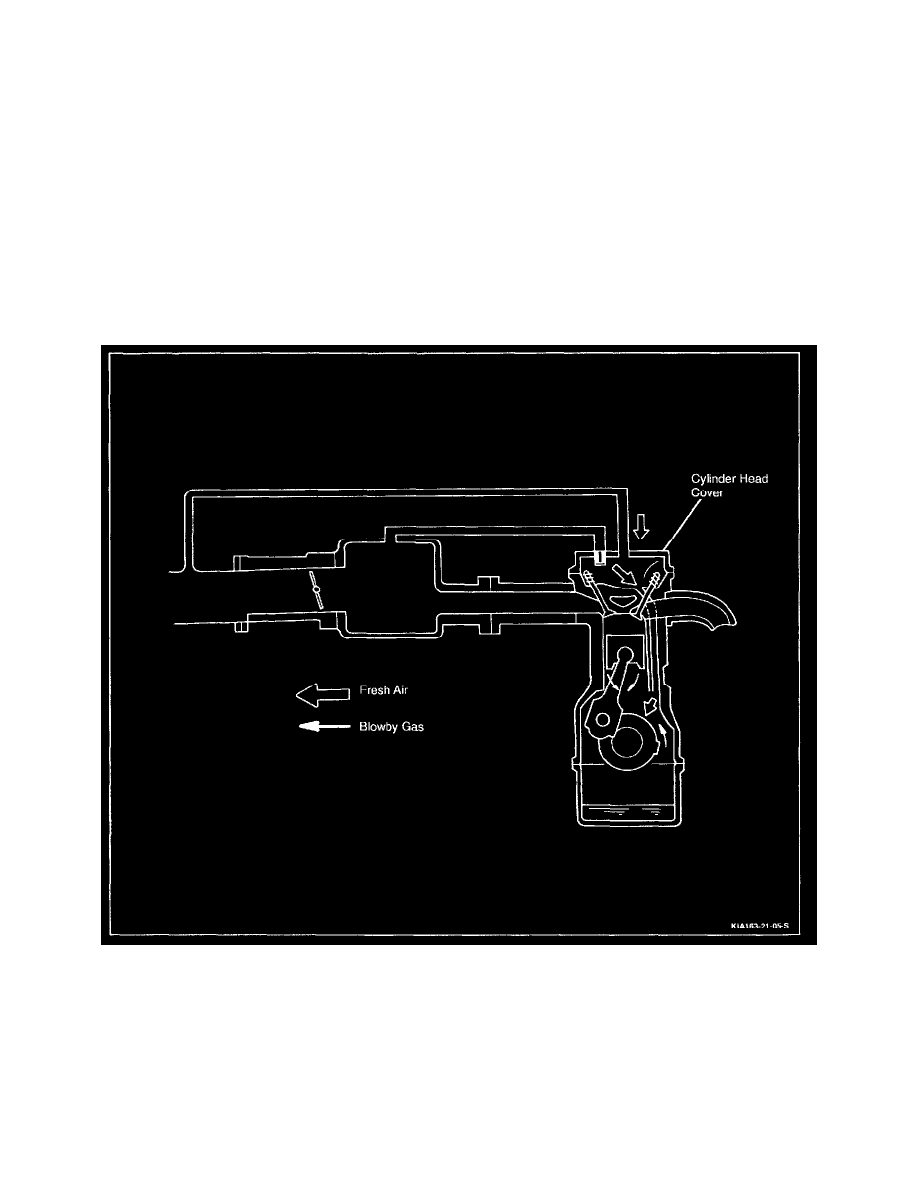
OPERATION
The ventilation process is as follows:
-
The crankcase control system controls these fumes or vapors (blow by) by directing them back into the engine where they are consumed in the
normal combustion process.
-
The crankcase ventilating vacuum source is the upper intake manifold.
-
The fresh air passes through the engine air cleaner (ACL) and then through the crankcase ventilation tubes which connect to the valve covers.
-
Ventilating air moves through the crankcase ventilation tubes and down through the oil return passage into the lower crankcase.
-
The air and crankcase gas mixture flows from the crankcase through the oil separator and oil separator hose to the positive crankcase ventilation
valve (PCV valve) and then into the upper intake manifold.
The PCV valve is operated by the intake manifold vacuum.
When the engine is running at idle, the PCV valve is opened slightly and a small amount of blowby gas is drawn into the combustion chamber to
be burned.
As the engine speed rises the PCV valve is opened further, allowing a larger amount of blowby gas to be drawn into the combustion chamber.
