Sportage 4WD 2Dr L4-2.0L (2002)
5. If the pedal height does not change, the unit is operating.
6. If there is a problem, check for damage to the check valve or vacuum hose, and check the connection. Repair if necessary and check once again.
If the nature of the problem is still not clear after the steps above, follow the more detailed check described below:
Method Using Tester
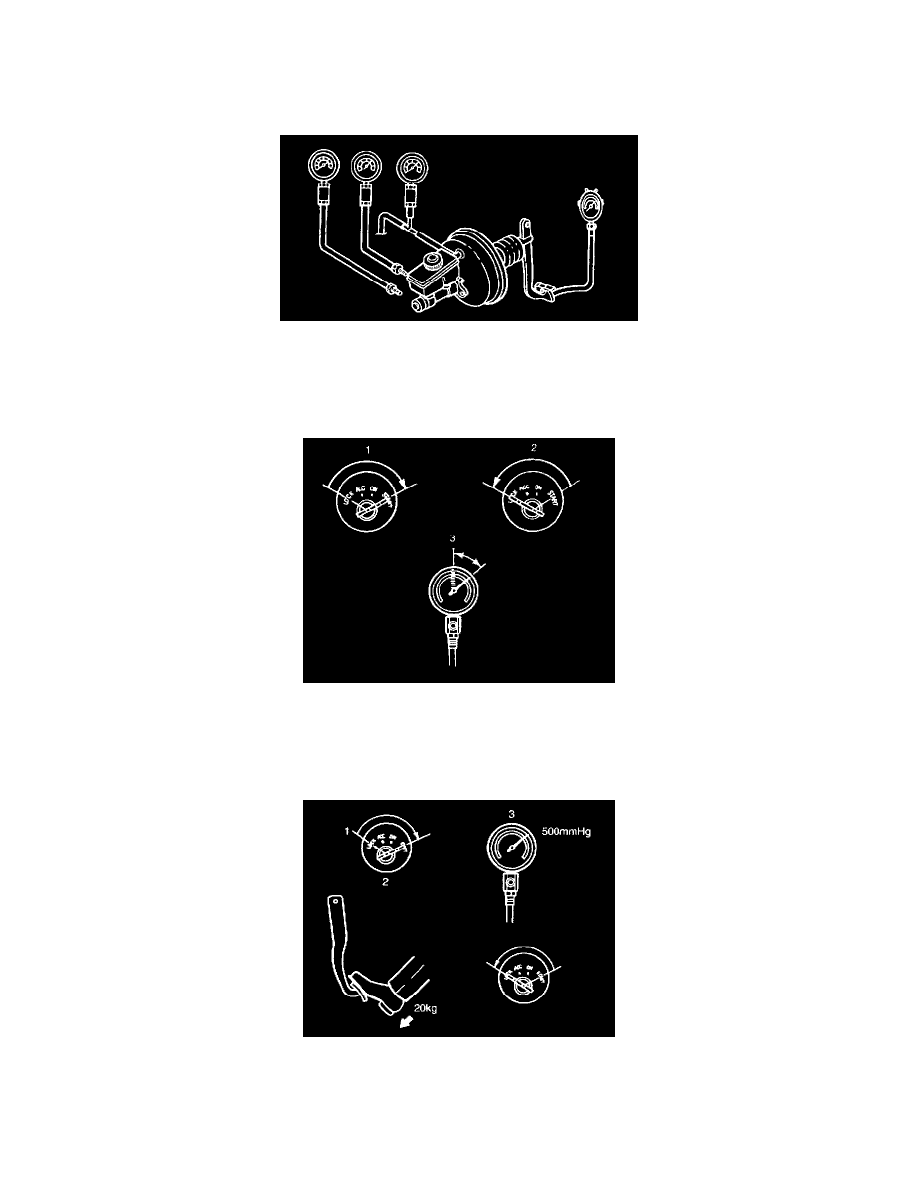
Connect a pressure gauge to the master cylinder, vacuum gauge to the vacuum booster and pedal depression force gauge to the brake pedal as
shown in the figure. After bleeding the air from the pressure gauge, conduct the test as described in the steps below.
Use commercially available gauges and pedal depression force gauge.
-
Checking for vacuum loss
Unloaded condition:
1. Start the engine.
2. Depress the brake pedal with a force of 44 lbs. (20 kg, 196 N).
3. Stop the engine when the vacuum gauge reaches 19.7 inHg (500 mmHg).
4. Observe the vacuum gauge for 15 seconds. If the gauge shows 18.7 - 19.7 inHg (475 - 500 mmHg), the unit is operating properly.
Loaded condition:
1. Start the engine.
2. Depress the brake pedal with a force of 44 lbs. (20 kg, 196 N).
3. With the brake pedal depressed, stop the engine when the vacuum gauge reaches 19.7 inHg (500 mmHg).
4. Observe the vacuum gauge for 15 seconds. If the gauge shows 18.7 - 19.7 inHg (475 - 500 mmHg), the unit is operating.
