Discovery II
COOLING SYSTEM - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
26-2-9
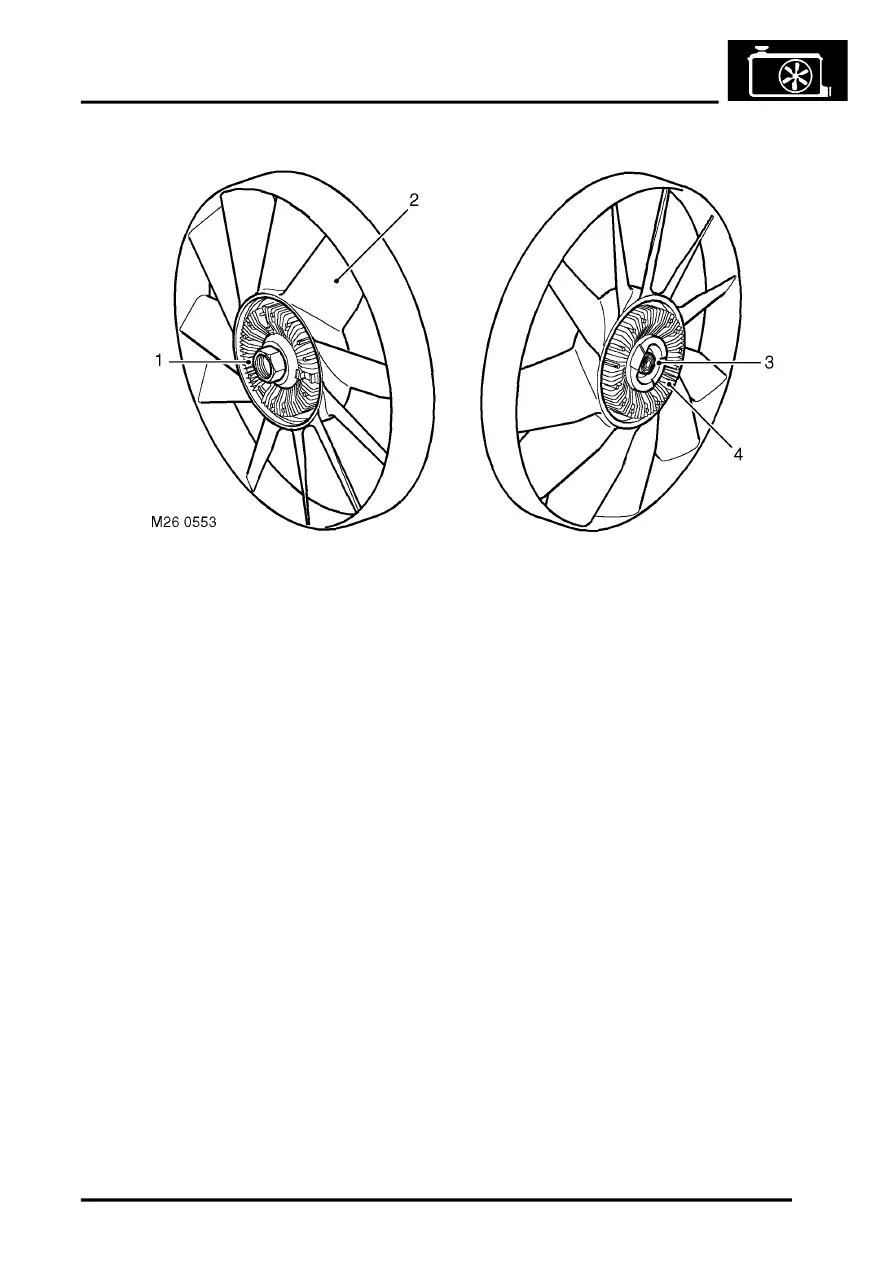
Viscous fan
1 Coolant pump pulley drive attachment
2 Fan blades
3 Bi-metallic coil
4 Body
The viscous fan provides a means of controlling the speed of the fan relative to the operating temperature of the
engine. The fan rotation draws air through the radiator, reducing engine coolant temperatures when the vehicle is
stationary or moving slowly.
The viscous fan is attached to the coolant pump drive pulley and secured to the pulley by a nut. The nut is positively
attached to a spindle which is supported on bearings in the fan body. The viscous drive comprises a circular drive
plate attached to the spindle and driven from the coolant pump pulley and the coupling body. The drive plate and the
body have interlocking annular grooves with a small clearance which provides the drive when silicone fluid enters the
fluid chamber. A bi-metallic coil is fitted externally on the forward face of the body. The coil is connected to and
operates a valve in the body. The valve operates on a valve plate with ports that connect the reservoir to the fluid
chamber. The valve plate also has return ports which, when the valve is closed, scoop fluid from the fluid chamber
and push it into the reservoir under centrifugal force.
Silicone fluid is retained in a reservoir at the front of the body. When the engine is off and the fan is stationary, the
silicone fluid level stabilises between the reservoir and the fluid chamber. This will result in the fan operating when the
engine is started, but the drive will be removed quickly after the fan starts rotating and the fan will 'freewheel'.
At low radiator temperatures, the fan operation is not required and the bi-metallic coil keeps the valve closed,
separating the silicone fluid from the drive plate. This allows the fan to 'freewheel' reducing the load on the engine,
improving fuel consumption and reducing noise generated by the rotation of the fan.
When the radiator temperature increases, the bi-metallic coil reacts and moves the valve, allowing the silicone fluid
to flow into the fluid chamber. The resistance to shear of the silicone fluid creates drag on the drive plate and provides
drive to the body and the fan blades.
