Range Rover P38
17
EMISSION CONTROL
NEW RANGE ROVER
34
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
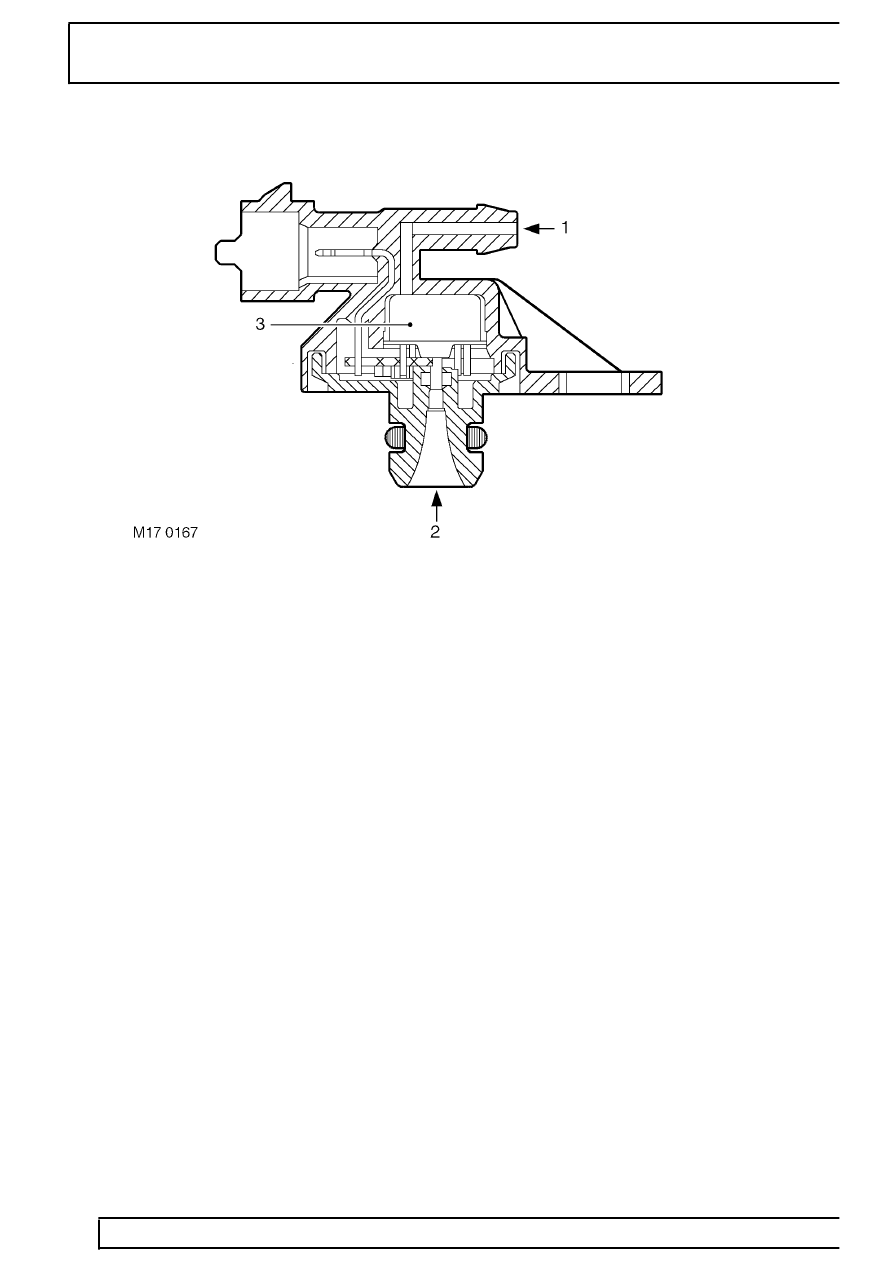
Fuel tank pressure sensor - (NAS only)
1. Ambient pressure
2. Tank pressure
3. Sensor cell
A fuel tank pressure sensor is fitted to NAS vehicles
with advanced EVAPS, it is used by the ECM during
an EVAP system leak test, in accordance with the on
board diagnostics (OBD) strategy.
The fuel tank pressure sensor is located in the top
flange of the fuel tank sender/ fuel pump module and
is a non-serviceable item (i.e. if the sensor becomes
defective, the entire fuel tank sender unit must be
replaced). The fuel tank pressure sensor connector is
accessible through the fuel pump access hatch in the
rear floor of the vehicle.
The pressure sensor is basically a piezo-resistive
sensor element with associated circuitry for signal
amplification and temperature compensation. The
active surface is exposed to ambient pressure by an
opening in the cap and by the reference port. It is
protected from humidity by a silicon gel. The tank
pressure is fed up to a pressure port at the rear side
of the diaphragm.
Fuel evaporation leaks are diagnosed by the ECM
monitoring the sensor for a drop in vacuum pressure
during test conditions. The EVAP system is sealed by
the CVS valve and purge valve after a vacuum has
been set up in the system from the intake manifold
while the purge valve is open and the CVS valve is
closed.
If any holes or leaks are present at the evaporation
system joints, the vacuum pressure will gradually drop
and this change in pressure will be detected by the
fuel tank pressure sensor. The system is sensitive
enough to detect leaks down to 1mm (0.04 in.) in
diameter.
The fuel tank pressure sensor is part of the NAS OBD
system, a component failure will not be noticed by the
driver, but if the ECM detects a fault, it will be stored in
the diagnostic memory and the MIL light will be
illuminated on the instrument pack. Possible failures
are listed below:
•
Damaged or blocked sensor
•
Harness/connector faulty
•
Sensor earthing problem
•
Open circuit
•
Short circuit to battery voltage
•
Short circuit to ground
•
ECM fault
