6 L4-2.5L (2010)
Compression Check: Testing and Inspection
COMPRESSION INSPECTION [L5]
WARNING:
-
Hot engines and oil can cause severe burns. Be careful not to burn yourself during removal/installation of each component.
-
Fuel vapor is hazardous. It can very easily ignite, causing serious injury and damage. Always keep sparks and flames away from fuel.
-
Fuel line spills and leakage are dangerous. Fuel can ignite and cause serious injuries or death and damage. Fuel can also irritate skin and eyes. To
prevent this, always complete the "Fuel Line Safety Procedure". See: Powertrain Management/Fuel Delivery and Air Induction/Service
Precautions/Vehicle Damage Warnings/Before Service Precaution
1. Verify that the battery is fully charged. See: Starting and Charging/Battery/Testing and Inspection
-
Recharge it if necessary. See: Starting and Charging/Battery/Service and Repair/Procedures
2. Warm up the engine to the normal operating temperature.
3. Perform "Fuel Line Safety Procedures". Leave the fuel pump relay removed. See: Powertrain Management/Fuel Delivery and Air
Induction/Service Precautions/Vehicle Damage Warnings/Before Service Precaution
4. Remove the plug hole plate. See: Service and Repair/Removal and Replacement/Plug Hole Plate Removal/Installation
5. Remove the ignition coils. See: Powertrain Management/Ignition System/Ignition Coil/Service and Repair
6. Remove the spark plugs. See: Tune-up and Engine Performance Checks/Spark Plug/Service and Repair
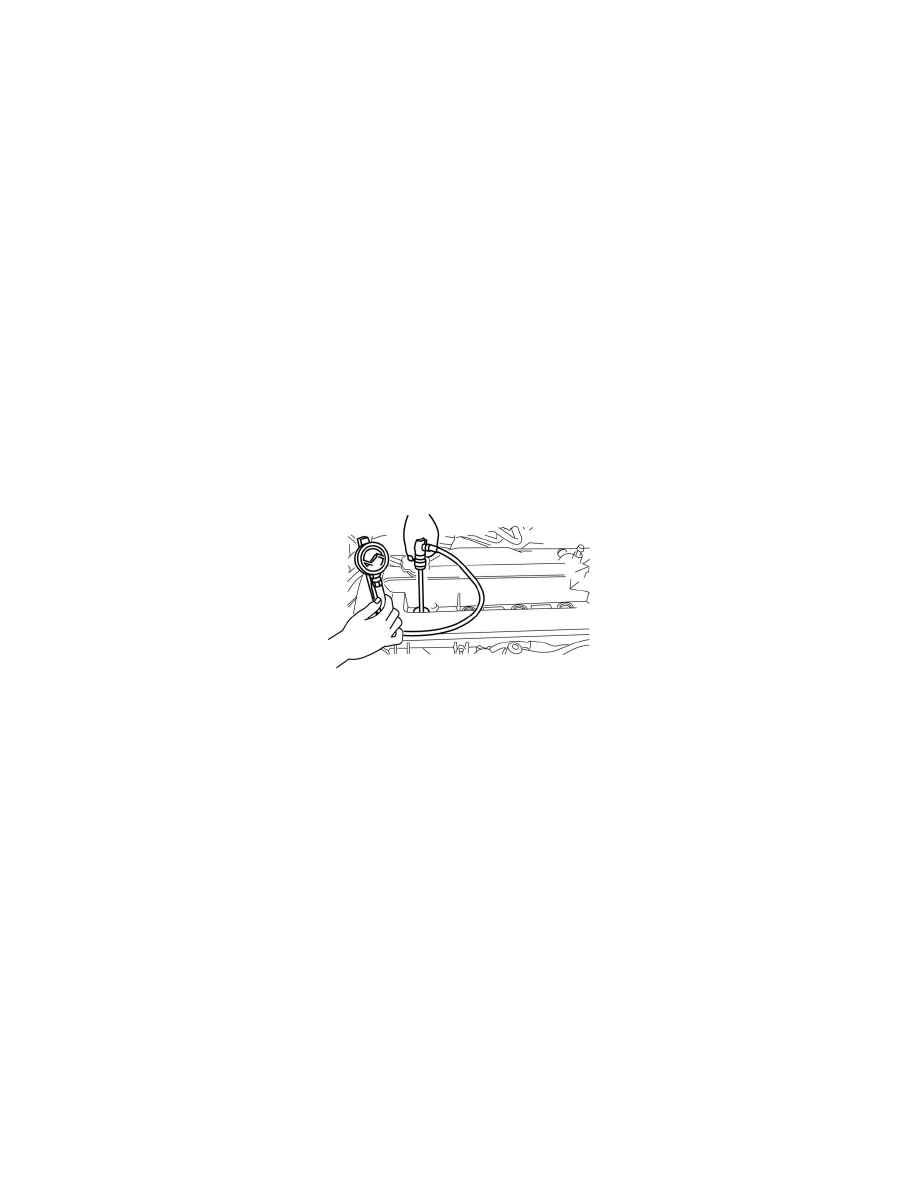
7. Connect a compression gauge into the spark plug hole.
8. Fully depress the accelerator pedal and crank the engine.
9. Note down the maximum gauge reading.
10. Inspect each cylinder as above.
-
If the measured value is less than the limited value, or there is a cylinder whose compression value varies from that of other cylinders by 196.1
kPa {2.0 kgf/cm2, 28.5 psi} or more, add a small amount of engine oil through the spark plug hole. Then measure the compression pressure
and perform the respective operations for the following cases.
-
If the compression increases, the piston, the piston rings, or cylinder wall may be worn and overhaul is required.
-
If the compression stays low, a valve may be stuck or improperly seated and overhaul is required.
-
If the compression in adjacent cylinders stays low, the cylinder head gasket may be damaged or the cylinder head distorted and overhaul is
required.
Compression
-
Standard: 1,324 kPa {13.50 kgf/cm2, 192.0 psi} [300 rpm]
-
Minimum: 927 kPa {9.45 kgf/cm2, 134 psi} [300 rpm]
-
Maximum difference between cylinders: 196.1 kPa {2.0 kgf/cm2, 28.5 psi}
11. Disconnect the compression gauge.
12. Install the following parts.
a. Spark plugs. See: Tune-up and Engine Performance Checks/Spark Plug/Service and Repair
b. Ignition coils. See: Powertrain Management/Ignition System/Ignition Coil/Service and Repair
