Raider V6-3.7L SOHC (2006)
Some examples of TCM indirect outputs are:
-
Transmission Temperature (to PCM)
-
PRNDL Position (to cluster/CCN)
In addition to monitoring inputs and controlling outputs, the TCM has other important responsibilities and functions:
-
Storing and maintaining Clutch Volume Indexes (CVI)
-
Storing and selecting appropriate Shift Schedules
-
System self-diagnostics
-
Diagnostic capabilities (with scan tool)
Note: If the TCM has been replaced, the "Quick Learn Procedure" must be performed. See: Testing and Inspection
Battery Feed
A fused, direct battery feed to the TCM is used for continuous power. This battery voltage is necessary to retain memory in the TCM. When the
battery (B+) is disconnected, this memory is lost. When the battery (B+) is restored, this memory loss is detected by the TCM and a Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) is set.
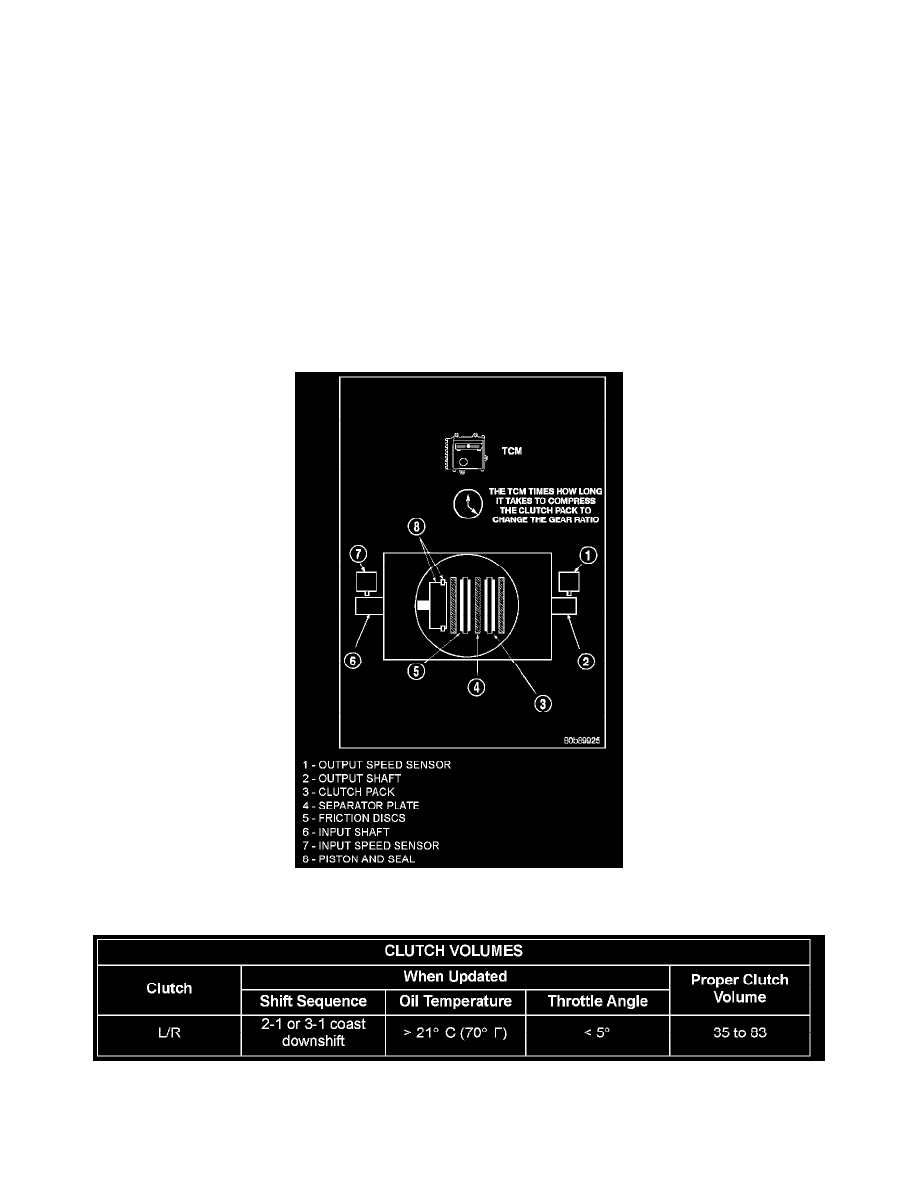
Clutch Volume Indexes (CVI)
An important function of the TCM is to monitor Clutch Volume Indexes (CVI).
CVIs represent the volume of fluid needed to compress a clutch pack.
42RLE Part 1
