| Leaks on the shock absorbers |
| Minor oil leakage (sweating) on the piston rod seal does not entail the replacement of the shock absorber. |
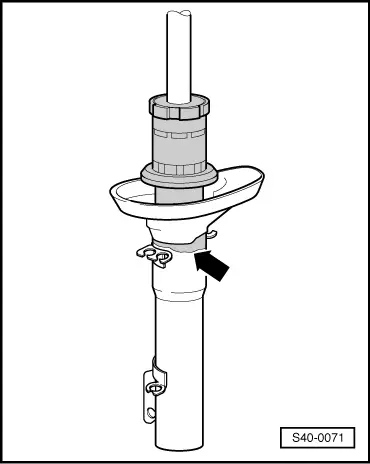
| If an oil leak is visible (but blunt, dull, possibly dried by dust) and does not propagate any further than from the top shock-absorber plug (piston rod seal) to the bottom spring cap -arrow-, the shock absorber is deemed to be O.K. |

Note | A slight oil leak is beneficial as the gasket is lubricated and this increases the life time. This applies for shock absorbers on the front as well as the rear axle. |
| Noises on the shock absorbers |
| Attention must be drawn to the fact that in the event of complaints about noise, the shock absorbers are very often regarded as being the source of noise. |

Note | In the event of complaints about noises interpreted as knocking or cracking noises, always first perform a test drive with the customer to determine where, when and how these noises occur (preferably on a bumpy dry road). |
| Inspect shock absorber without gas pressure |
| Defective shock absorbers become noticeable while driving because of the knocking noises - caused by wheel hopping - more specifically on poor road and they must be replaced. The failure is mainly caused by the loss of oil. The shock absorber then compresses and/or expands in jolts. It has an "idle travel" before taking effect. |

Note | Shock absorbers are maintenance-free. It is not possible to top up the shock absorber oil. |
| Inspect shock absorber with gas pressure |
| Defective shock absorbers with gas pressure are also noticeable because of loud knocking noises caused by wheel hopping and externally usually exhibit considerable oil leakage. |
| Manual testing, as described below, can determine if the shock absorber is damaged or not: |
| –
| Compress the shock absorber by hand. |
| –
| While doing so, the piston rod can be moved during the entire stroke time with a uniform resistance and without jerking. |
| –
| Release the piston rod. On sufficiently pressurized shock absorbers it will automatically return to its original position. |
| –
| If this is not the case, the shock absorber need not necessarily be replaced, as it will still operate as a conventional shock absorber (see instructions below). |

Note | t
| The absorbing function is still fully present without gas pressure as long as the oil leakage is not too important. However, the noise intensity can deteriorate. On older vehicles it is possible to continue using an operational yet pressureless shock absorber without problem. |
| t
| The spring shock absorbers with gas pressure are only installed on the rear axle. |
| t
| The gas pressure in the shock absorber improves the noise behaviour and the function when driving over poor road surfaces. |
|
|
|
 Note
Note Note
Note Note
Note Note
Note
 Note
Note Note
Note Note
Note Note
Note