XC90 AWD L6-3.2L VIN 98 B6324S (2007)
connected cable between the engine control module (ECM) and transmission control module (TCM). Also see Design and Function, transmission
control module (TCM).
Camshaft control (CVVT)
Only the intake camshaft can be controlled by the Engine control module (ECM) via a reset valve.
The intake camshaft is located in the engine's leading edge (in the travel direction) and the exhaust camshaft in the trailing edge (towards the passenger
compartment). The camshafts are divided into two banks:
Bank 1, cylinder 1, 2, 3.
Bank 2, cylinder 4, 5, 6.
The camshafts are driven by the crankshaft via a gear housing located on the engine's top side.
When each camshaft is adjusted in the factory, its position is aligned with the crankshaft's position. The camshaft's position at alignment against the
crankshaft is called the camshaft's 0-position (basic setting).
At camshaft control (CVVT), the camshaft's 0-position is displaced so that the camshaft's angle position is changed. Thus, opening and closing of the
exhaust and inlet valves changes relative to the crankshaft.
By controlling the camshaft's angle position, the engine's performance can be increased, idle quality can be improved, and emissions can be reduced.
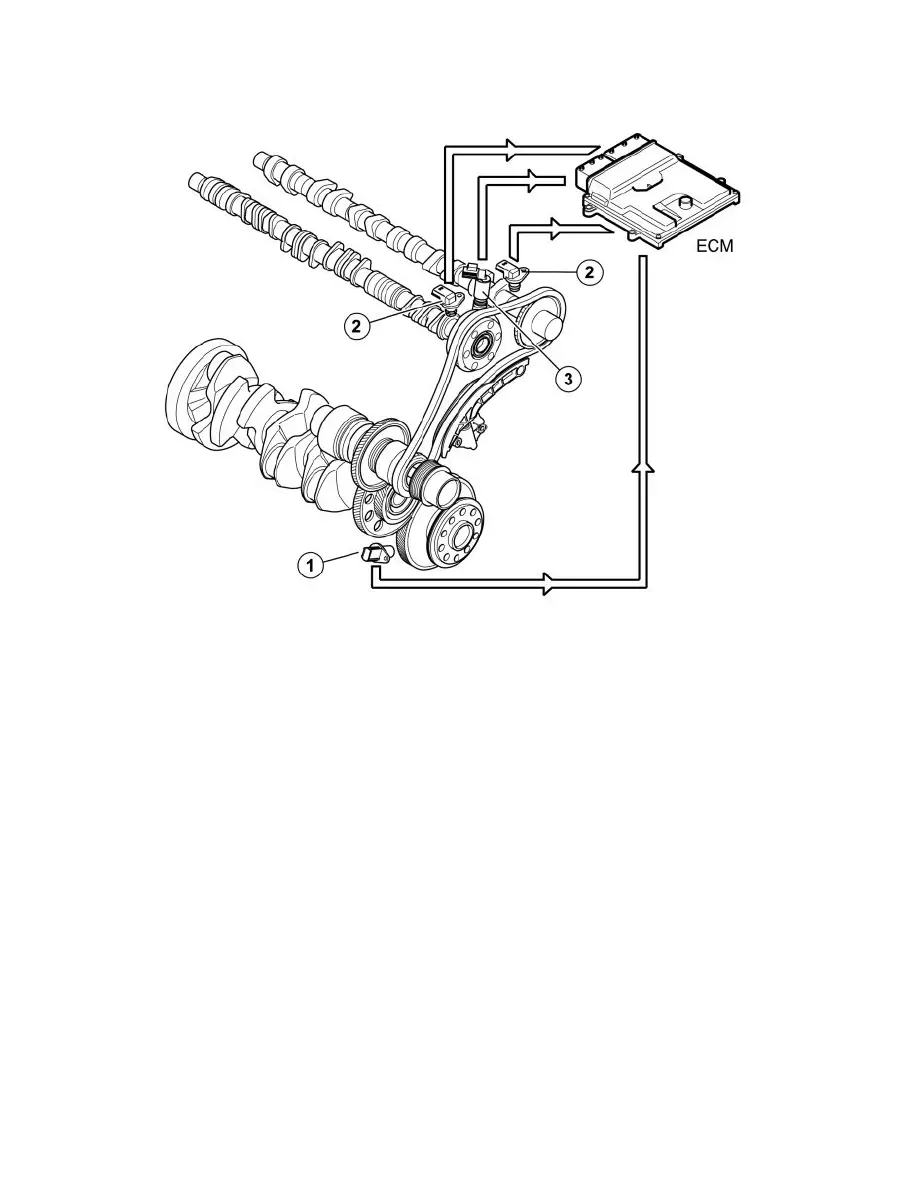
The engine control module (ECM) detects the position of the camshafts by comparing the signals from the engine speed (RPM) sensor (1) (crankshaft
position) and the camshaft position (CMP) sensors (2) (camshaft positions). The engine control module (ECM) then controls the angle of the camshaft
by controlling the oil flow to the CVVT unit using the reset valve camshaft (3).
There are diagnostics for this function. See also: Camshaft diagnostics (CVVT) See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control
Systems/Description and Operation/Camshaft Diagnostics (CVVT)
Controlling, reset valve camshaft
