XC90 AWD V8-4.4L VIN 85 B8444S (2005)
If the signal from the engine speed (RPM) sensor is incorrect or missing, the control module will use signals from the camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
The engine speed (RPM) sensor can be diagnosed by the engine control module (ECM) and the sensor signal (engine speed (RPM)) can be read off.
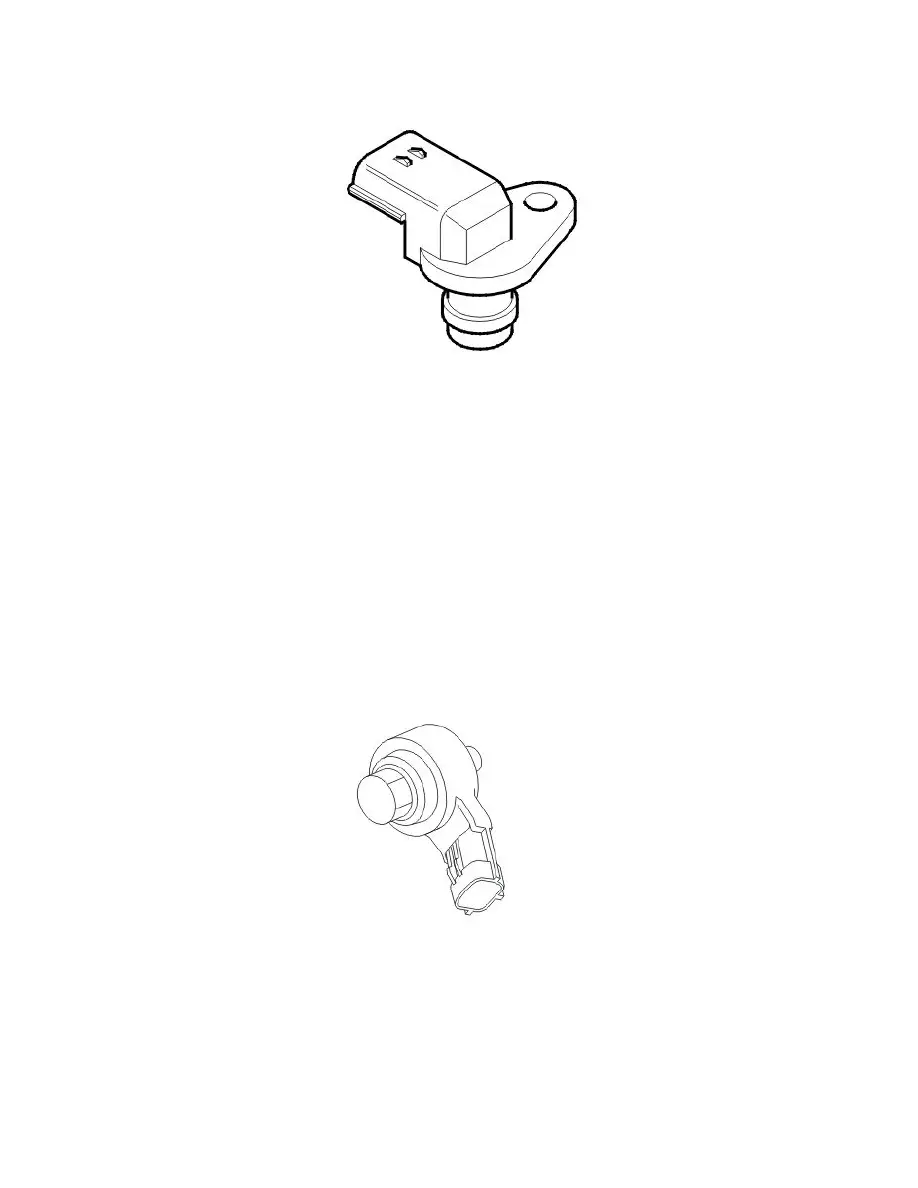
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor
The function of the camshaft position (CMP) sensor is to detect the flanks of the camshaft rotor. The signal from the sensor is used by the engine control
module (ECM) to determine the angle of the camshaft.
Each camshaft is divided into a number of flanks (segments) per camshaft revolution. A pulse wheel on the camshaft consisting of teeth (the teeth are
positioned by each flank) is used by the camshaft position sensor (CMP) to detect the flanks and the position of the camshaft.
In the event of misfire or engine knock, the control module is able to determine which cylinder is misfiring or knocking using the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor signal. Also see Knock sensor (KS) and Engine speed (RPM) sensor.
Data about the camshaft position is used during camshaft control (CVVT). See: Function, B8444S See: Powertrain Management/Computers and Control
Systems/Description and Operation/Engine Control Module (ECM)/Function
The sensor, which is a magnetic resistor with a permanent magnet, is grounded in the control module and supplied with 5 V from the control module.
When one of the teeth on the camshaft pulse wheel passes the camshaft position (CMP) sensor, a signal is transmitted to the control module from the
camshaft position (CMP) sensor. The signal varies between 0 - 5 V and is high when a tooth is close to the camshaft position (CMP) sensor and low
when the tooth leaves the camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
There is camshaft position (CMP) sensor for each camshaft.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensors are located by the camshafts on the rear edge of the engine (left-hand side of the vehicle, closest to the flywheel).
The engine control module (ECM) can diagnose the camshaft position (CMP) sensors.
Knock sensor (KS)
The function of the knock sensor (KS) is to monitor combustion knocking from the engine. Knocking may damage the engine and reduces the efficiency
of engine combustion.
If the engine control module (ECM) registers knocking from any of the cylinders, the ignition will be retarded for that cylinder at the next combustion
stage. If repeated ignition retardation does not prevent knocking, the injection period will be increased. This has a cooling effect.
The sensor is made up of Piezo electrical crystals. If there is engine knock, vibrations (sound waves) spread through the cylinder block to the knock
sensor (KS). The resultant mechanical stress in the Piezo electrical material in the knock sensors generates a voltage. This signal is transmitted to the
engine control module (ECM). The signal corresponds to the frequency and amplitude of the sound waves. This allows the Engine Control Module
(ECM) to determine if the engine is knocking. The camshaft position (CMP) sensor and engine speed (RPM) sensor are used to determine the operating
cycle of the engine (which cylinder is igniting) and therefore which cylinder is knocking.
The knock sensors are located on the engine block between the cylinder rows.
Knock sensor 1 detects knock on cylinders 5, 6, 7 and 8. Knock sensor 2 detects knock on cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4.
