LR3/Disco 3
maximum for advancing and 0.7 second maximum for retarding. While the valve timing is in the retarded mode, the ECM
produces a periodic lubrication pulse. This momentarily energises the valve timing solenoids to allow a spurt of oil into the
valve timing units. The lubrication pulse occurs once every 5 minutes.
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) VALVE
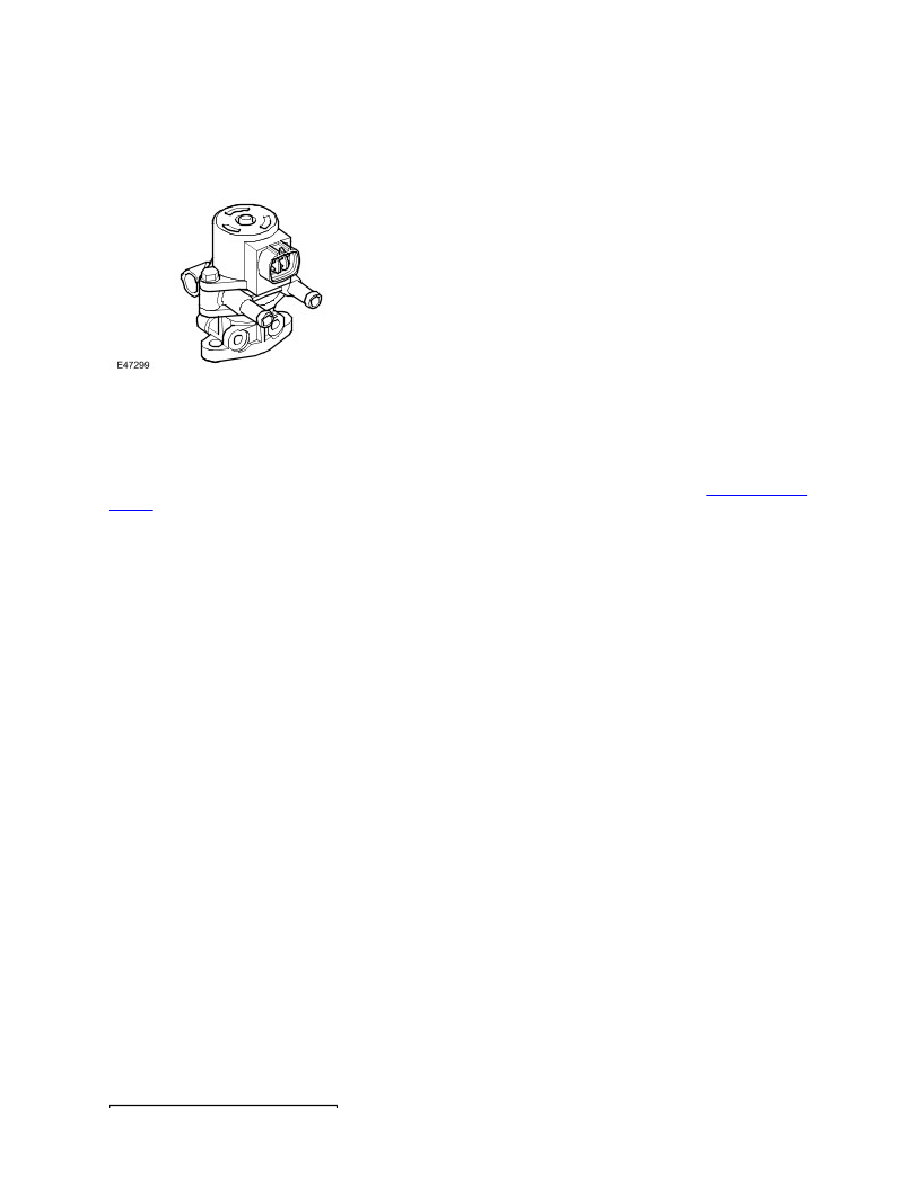
The Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve is an electrically controlled valve that allows burned exhaust gas to be
recirculated back into the engine. The EGR valve consists of a stepper motor that opens and closes the valve in steps.
Since exhaust gas has much less oxygen than air, it is basically inert. It takes the place of air in the cylinder and reduces
combustion temperature. As the combustion temperature is reduced, so are the oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
The EGR valve is located on the intake manifold with a pipe connecting the exhaust manifold to the valve. Connection
between the sensor and the harness is via a six-way connector. For additional information, refer to
Engine Emission
Control
(303-08B Engine Emission Control - 4.4L)
ECM ADAPTIONS
The ECM has the ability to adapt the values it uses to control certain outputs. This capability ensures the EMS can meet
emissions legislation and improve the refinement of the engine throughout its operating range.
The components which have adaptions associated with them are:
The APP sensor
The HO2S
The MAF/IAT sensor
The CKP sensor
Electric throttle body.
UHEGO/HEGO and MAF/IAT Sensor
There are several adaptive maps associated with the fuelling strategy. Within the fuelling strategy the ECM calculates
short-term adaptions and long term adaptions. The ECM will monitor the deterioration of the oxygen sensors (HEGO and
UHEGO) over a period of time. It will also monitor the current correction associated with the sensors.
The ECM will store a fault code in circumstances where an adaption is forced to exceed its operating parameters. At the
same time, the ECM will record the engine speed, engine load and intake air temperature.
CKP Sensor
The characteristics of the signal supplied by the CKP sensor are learned by the ECM. This enables the ECM to set an
adaption and support the engine misfire detection function. Due to the small variation between different flywheels and
different CKP sensors, the adaption must be reset if either component is renewed, or removed and refitted. It is also
necessary to reset the flywheel adaption if the ECM is renewed or replaced. The ECM supports four flywheel adaptions
for the CKP sensor. Each adaption relates to a specific engine speed range. The engine speed ranges are detailed in the
table below:
