Leon Mk1
|
 Note
Note
|
|
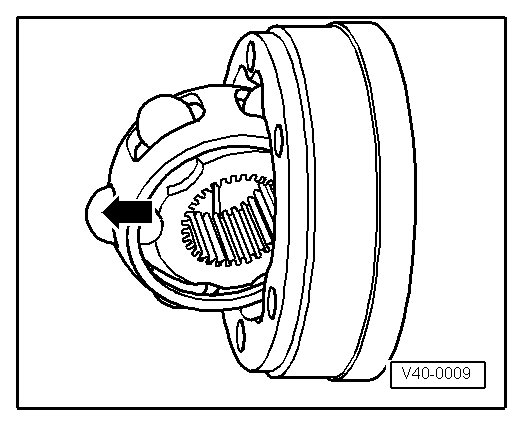
 Note
Note
|
|
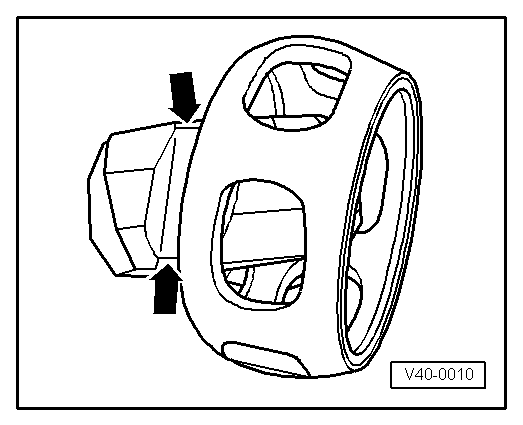
 Note
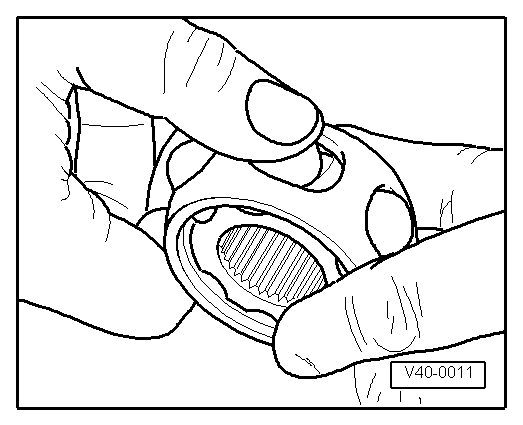
Note |
|
|
|
|
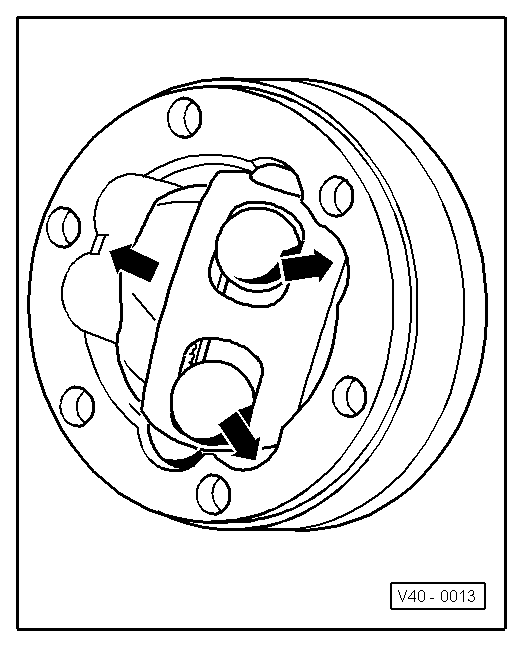
|
|
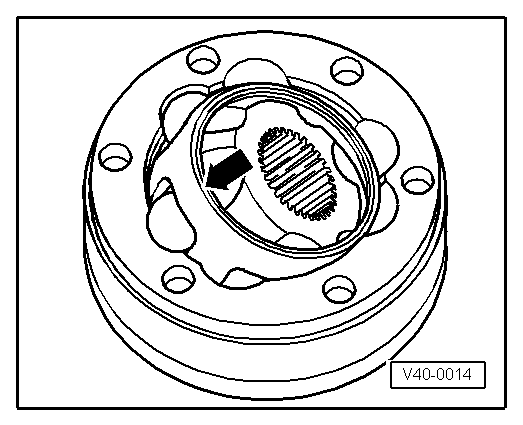
|
|
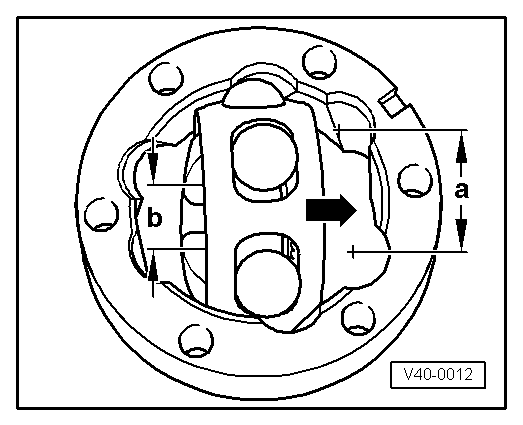
 Note
Note
|

|
 Note
Note
|

|
 Note
Note |

|
|

|
|

|
|

|