940 L4-2.3L SOHC VIN 88 B230F (1992)
A cold battery requires a higher charging voltage, therefore the voltage regulator is equipped with a bimetallic spring which, as the temperature
decreases, increases the pressure against the lower contact (2) thereby increasing the control voltage.
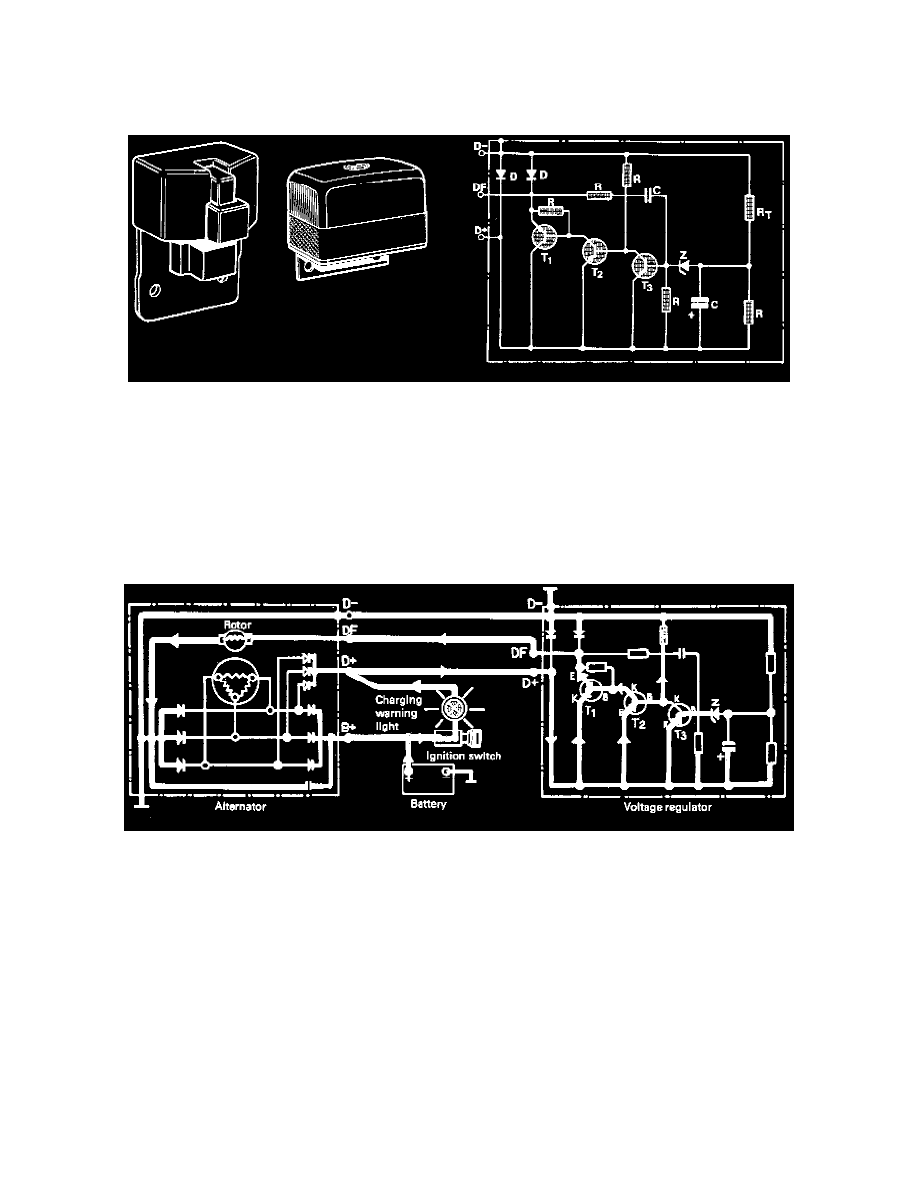
Inner circuit of transistor voltage regulator
Transistor voltage regulator
Z
Zener diode
D Diode
R Resistance
RT Thermistor
T
Transistor (1-3)
C Condenser
Operation
Ignition on, engine not running
A small current passes through the ignition switch, charging warning light, and the voltage regulator to the car's ground through the rotor winding. This
small current is the source of the magnetic field in the rotor which is necessary to initiate charging by the alternator.
Function
In the voltage regulator current passes from terminal D+ through transistor T2 (in via emitter E and out via base B). Transistor T2 then transfers current
through collector K to transistor T1 which will open and transfer exciter current to the rotor via DF.
