XC70 AWD L6-3.2L VIN 98 B6324S (2009)
General
Fuel pressure regulation for demand controlled fuel pumps means that the fuel pressure/flow is controlled steplessly by varying the output of the fuel
pump. The design of the system means that the fuel pressure can be regulated between 300 and 500 kPa. The high pressure is used in extreme situations,
such as heavy engine load for example and hot starts.
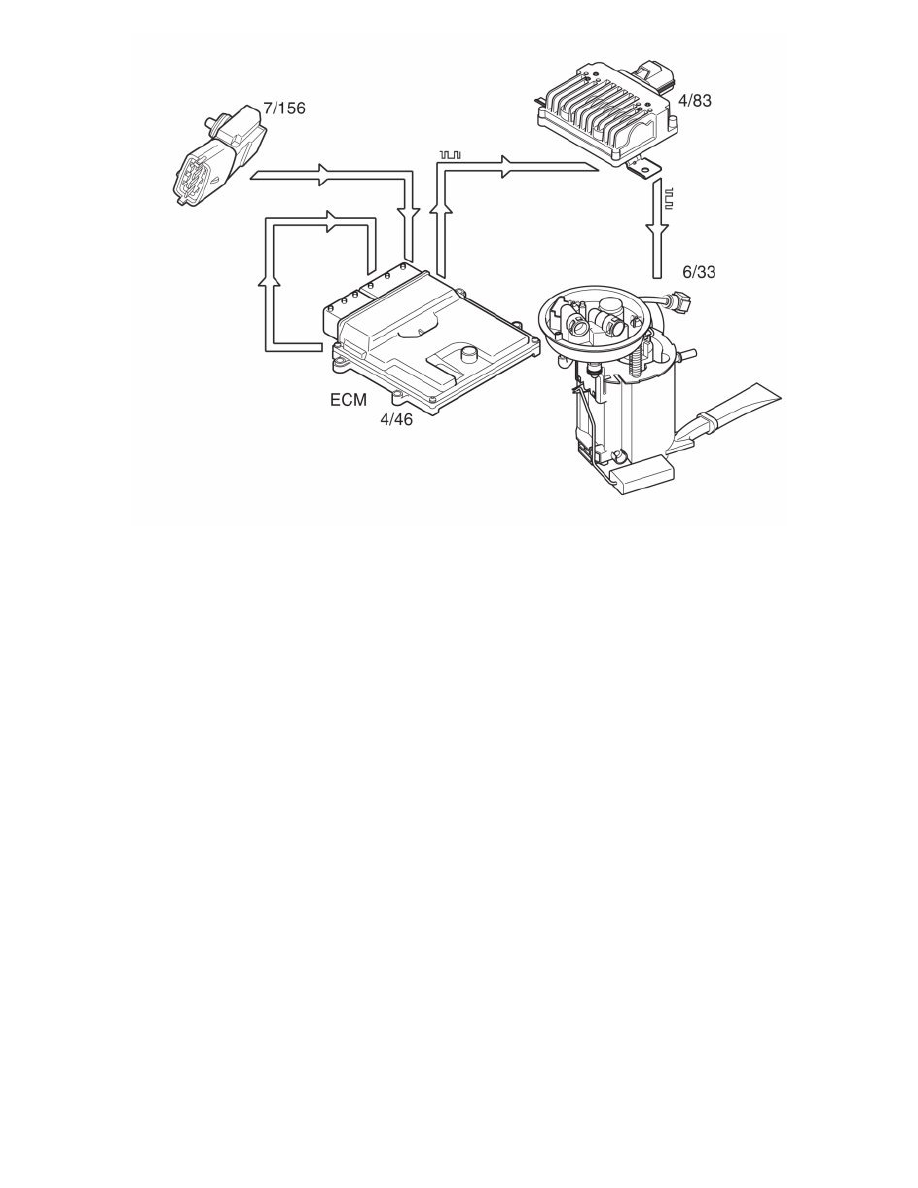
The following components are used for fuel pressure regulation:
-
engine control module (ECM) (4/46)
-
fuel pump control module (4/83)
-
fuel pressure sensor with fuel temperature sensor (7/156)
-
fuel pump (FP) (6/33).
The time taken for the engine start procedure can be reduced by rapidly increasing the pressure in the fuel rail when the engine control module (ECM)
receives a signal about the position of the start control module (SCU) from the central electronic module (CEM).
The injection period for the injectors can be better calculated by the engine control module (ECM) since the signal from the fuel pressure sensor
provides information regarding actual fuel pressure and temperature. Special cold starting properties for the engine are improved.
The advantages of varying the output of the fuel pump so that it is not always at full power are:
-
the total power consumption of the fuel pump (FP) is reduced, reducing the load on the power supply system and reducing fuel consumption
-
the service life of the fuel pump (FP) is increased
-
fuel pump noise is reduced.
Control
The engine control module (ECM) calculates the desired fuel pressure. A signal is then transmitted to the fuel pump control module indicating the
desired fuel pressure. Serial communication between the engine control module (ECM) and the fuel pump control module is used to carry the signal. The
fuel pump control module then operates the fuel pump unit to obtain the desired pressure using a pulse width modulation (PWM) voltage on the ground
lead. The fuel pump (FP) can be controlled steplessly by changing the pulse ratio of the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal. Only that pressure which
is required at that specific time will then be released to the fuel rail/injectors. The value of the pulse width modulation (PWM) signal is a measurement of
the operational load of the fuel pump (FP) (% duty, 100% = maximum pressure).
The engine control module (ECM) continuously monitors the fuel pressure using the signal from the fuel pressure sensor. This allows the desired fuel
pressure to be reached, and if necessary a signal is transmitted to the fuel pump control module requesting that the fuel pressure is adjusted. The engine
control module (ECM) regulates stable fuel pressure (approximately 400 kPa relative to the atmospheric pressure with the engine running).
Passive safety
For safety reasons, central electronic module (CEM) shuts off the fuel pump (FP) if the supplemental restraint system module (SRS) detects a collision.
